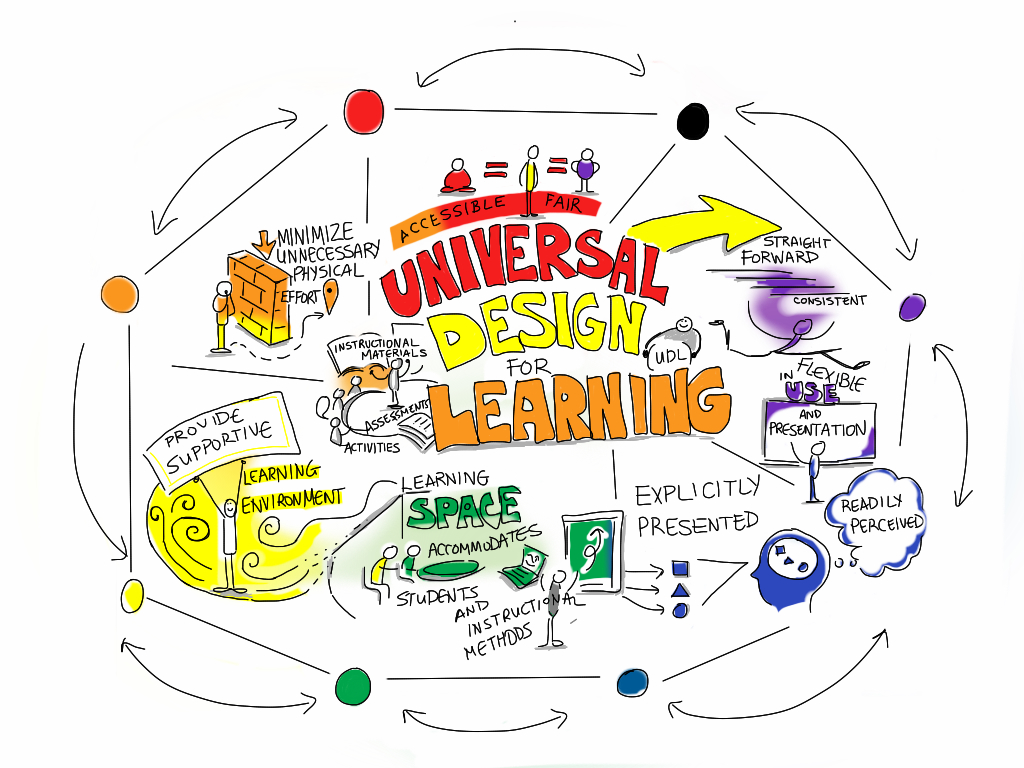
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) in Physical Education
What is UDL?
UDL is meant to create educational experiences that accommodate diverse needs of learners. UDL emphasizes the use of flexible teaching methods and strategies to ensure that every student is given fair access to learning opportunities.
Applying UDL in Physical Education
Teaching gym, applying UDL is important for creating accessibility while providing tools for physical and mental well-being. In EPHE, I’ve learned how to adapt activities to make them more inclusive for both physical and mental differences in students.
Inclusive Strategies in PE
With UDL, changes can be suggested such as using larger or lighter balls, visual markers on courts, or sensory-friendly spaces. Like what we’ve explored in EPHE, UDL ensures that students with physical or cognitive disabilities can always fully participate. Consider this video, How Inclusive Physical Education in School Benefits All Students which reviews how physical education enhances well being and leads to a more positive self image for students. The video discusses how good nutrition and adequate physical education helps benefit in the classroom as well. Physical inactivity can lead to obesity in disabled children. We need to have before, during, and after school movement time. At a young age, what children learn will impact them later on. Regardless of ability, all children deserve to be interacted with. As educators, it’s out job to help foster an inclusive environment at all levels.
UDL and Health Promotion
UDL principles make communities healthier and more inclusive through health promotion. UDL principles can provide credible ideas that can go on brochures, social media accounts or websites that are accessible to people with differing needs. Using UDL in my lesson plans to cater to the needs of my students, I’ll be able to ensure that all people, especially those with barriers (visible or non-visible), can develop health literacy. Because I want to teach high school, I’ll be looking specifically at active living 11.
Core Competencies in Active Living 11
The BC Curriculum includes core competencies of communication, personal and social, and thinking. It promotes active living, health literacy, and lifelong skills to empower students to make informed decisions about their health. The curriculum is designed with flexibility to accommodate unique needs, leading to greater levels of inclusivity throughout high schools across the province. The curriculum integrates health and wellbeing, safety, and participation as its curricular competencies. These competencies support self-reflection, decision-making, and interpersonal skills.
Big Ideas in the Curriculum
The curriculum is organized around “Big Ideas” that emphasize overall well-being. These “Big Ideas” include physical activity as an important part of overall health and well-being, finding enjoyable recreational activities that can motivate people to participate more regularly in physical activity, and safety and injury prevention practices which allow lifelong participation in physical activities. These big ideas, combined with curricular competencies listed on the curriculum guide for active living 11, provide a strong outline for how I can improve the lives of my future students. I will keep these principles at the forefront of my mind when designing lesson plans and ensure that positive health behaviors are being modelled through my own actions as an individual. I strongly believe that as a high school teacher, I’ll be able to share my health struggles/journey with my students and be able to provide tools that helped me to hopefully help a future teenager get well too. 😊
The Comprehensive School Health (CSH) Model
The CSH model is a whole school approach that supports healthy school communities. It emphasizes collaboration among students, educators, families, and the broader community, recognizing that health and learning are deeply interwoven. The CSH model can be applied in various settings, especially in schools where there are anti-bullying initiatives and spaces for physical activity, such as playgrounds or gyms, that promote a sense of belonging. My elementary school had a “lonely bench,” where students who didn’t have a lot of friends could sit and then be approached by other students or staff to brighten their day. This contributed to my elementary school’s social environment, which is an important part of CSH. To incorporate a holistic framework into my teaching, with guidance from the curriculum competencies discussed above, I’ll strive to instruct students about physical activity, nutrition, mental health, and relationships in interactive lessons involving hands-on workshops or field trips where wellness can be explored and freely discussed. Additionally, using collaboration and leadership, as a teacher I’ll want to make sure policies are introduced that prioritize health, such as guidelines for healthy snacks, mental health days, or physical activity breaks. I believe teachers deserve mental health days as well and will fight for this. As someone with celiac disease, part of what I’ll propose to my school with the CSH model in mind will be to make sure snacks are inclusive of students with severe allergies. Making a lasting impact in schools is something I’m excited about when entering a district.
Quality Daily Physical Education (QDPE) and Inclusivity
QDPE supports lifelong engagement in physical activity and contributes to a healthy, active society. QDPE goes with this blog post’s theme of fostering inclusivity. There are many benefits in QDPE, for example, there’s enhanced skill development, increased motivation towards activity, positive long term health impacts and more. In the classroom, it contributes to a positive environment where there is encouragement towards teamwork and sportsmanship, building a sense of belonging. Outside of schools, in the community QDPE can offer accessible programs that teach fundamental movement skills. This is huge for children and youth in Victoria who may be limited by what their parents have taught them or even have financial barriers. These programs can help ensure that people, regardless of ability, age, or even situation can participate in sport.
Final Thoughts
Developing physical literacy and implementing QDPE are essential for sparking a desire for lifelong engagement in physical activity, which leads to improved health and wellness. By promoting skill development, confidence, and inclusivity, opportunities are created for students and community members to join, learn, be challenged, and move together through collective acceptance of the benefits of movement and wellness.
Thank you for reading my second blog post!


Citations:
Benefits of QPE. (n.d.). PHE Canada. https://phecanada.ca/professional-learning/qdpe/benefits-qdpe
Building Student Success – B.C. curriculum. (n.d.). https://curriculum.gov.bc.ca/curriculum/physical-health-education/11/active-living
What is Comprehensive School Health? (n.d.). https://education.alberta.ca/comprehensive-school-health/what-is-comprehensive-school-health/